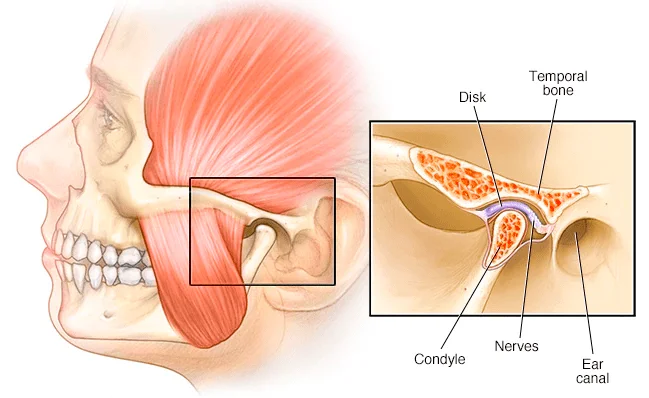
What is Blue Light?
Blue light is everywhere around us! It is particularly found in sunlight and LEDs. We tend to get the most exposure to blue light outdoors. Some artificially created indoor sources of blue light also include LED lighting emitted from our televisions. Compared to our ancestors, our lifestyles have evolved in more ways resulting in greater exposure to the sun and increasing usage of LED lighting, leading to a greater risk of health issues.
Blue light is an umbrella term referring to different light variations. It is just one part of the spectrum of light emitted. The most harmful is blue-violet light as it is a contributing factor to age-related macular degeneration and damages the retina. As almost all visible blue light passes through the cornea and lens and reaches the retina, this light may affect vision and could prematurely age the eyes. Too much exposure to blue-violet light could lead to digital eyestrain whereby blue light from screens and digital devices can decrease eye contrast. Fatigue, dry eyes, bad lighting, and poor posture in front of the computer can also cause eyestrain.
However, it is important to note that not all blue light is harmful! Some blue light exposure is essential for good health. One variation is the blue-turquoise light that enhances our cognitive and sleep behaviour. This light boosts alertness, helps memory and cognitive function, and elevates mood. It is also very important in regulating our circadian rhythm — the body’s natural wakefulness and sleep cycle. Exposure to blue-turquoise light during daytime hours helps maintain a healthy circadian rhythm but too much late at night can potentially cause sleepless nights and daytime fatigue.
How to protect yourself from blue light at night?
– Use dim red lights for night lights. Red light has the least power to shift circadian rhythms and suppress melatonin.
– Avoid looking at screens 2 to 3 hours before bed.
– Consider wearing blue-blocking glasses or installing an app on your electronic devices that filters the blue/green wavelength at night.
Experiencing Physical Strain from Screen Use?
Extended screen time and blue light exposure may contribute to more than just eye fatigue. It can also affect posture, tension, and sleep quality. An osteopathic assessment may help address underlying physical strain linked to modern lifestyle habits. Learn more about consulting an osteopath in Singapore.