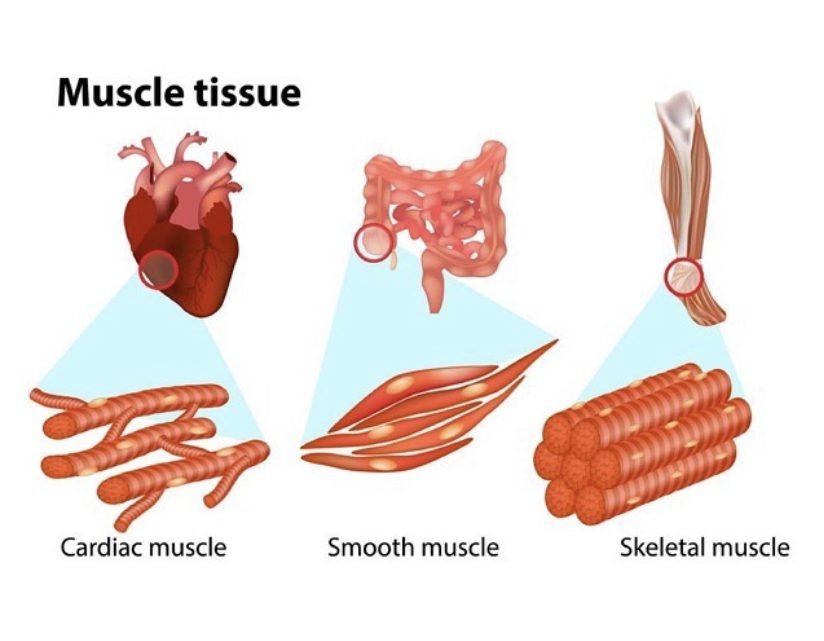
Types of Muscle Tissues
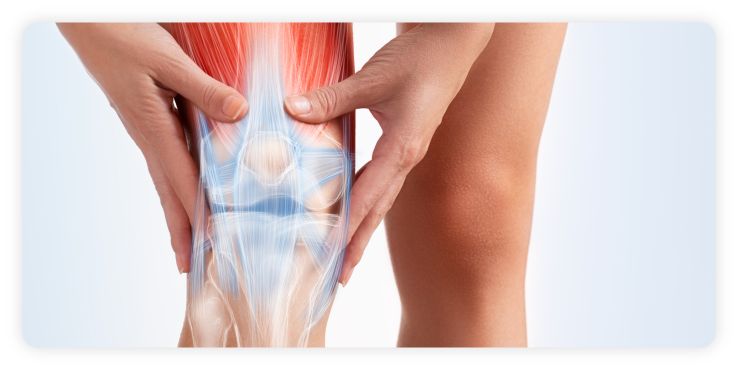
Did you know that actually about half of the body’s weight is muscle? In the human muscular system, the muscle tissue is categorised into three distinct types – skeletal, smooth and cardiac.
There are over 650 skeletal muscles that move bones and other structures. Also known as voluntary muscles, skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and produce all the movements of body parts in relation to each other. These muscles can also be used in involuntary reflex responses when a fast movement is required. For example, they will respond rapidly to instant chemical and electrical impulses from the brain when touching a hot stove by withdrawing the hand from the dangerous situation without conscious thought.
Smooth muscle is an involuntary muscle found in the walls of hollow organs throughout the body. Smooth muscle contractions are movements triggered by impulses that travel through the autonomic nervous system to the smooth muscle tissue. The arrangement of cells within smooth muscle tissue allows for contraction and relaxation with great elasticity. The smooth muscle in the walls of organs like urinary bladder and uterus allows those organs to expand and relax as needed. The smooth muscle of the alimentary canal (digestive tract) facilitates the peristaltic waves that move swallowed food and nutrients. In the eye, smooth muscle changes the shape of the lens to bring objects into focus. Artery walls include smooth muscle that relaxes and contracts to move blood through the body.
Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart and is an involuntary muscle, which contracts in response to signals from the cardiac conduction system to make the heart beat. The heart wall is composed of three layers. The middle layer, the myocardium is responsible for the heart’s pumping action. Cardiac muscle is made from cells called cardiocytes which have a striated appearance. Cardiocytes are branched, allowing them to connect with several other cardiocytes, forming a network that facilitates coordinated contraction.