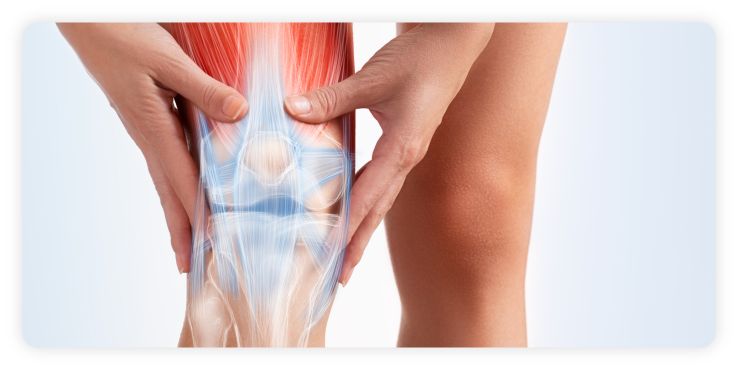
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of one or more of the joints. The main symptoms of Arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. In some cases, working with an osteopath in Singapore may help manage symptoms by improving joint mobility and reducing surrounding muscle tension.
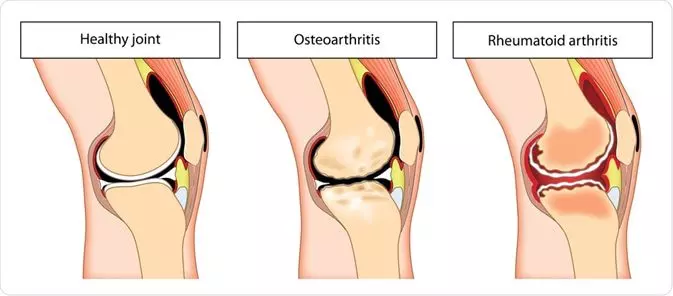
Osteoarthritis
The most common type of arthritis is Osteoarthritis. This involves wear-and-tear damage to the joint’s cartilage which is the hard, slick coating on the ends of bones where they form a joint. Cartilage cushions the ends of the bones and allows nearly frictionless joint motion, but enough damage can result in bone grinding directly on bone, which causes pain and restricted movement. This wear-and-tear can occur over many years, or it can be hastened by a joint injury or infection. Osteoarthritis also affects the entire joint. It causes changes in the bones and deterioration of the connective tissues that attach muscle to bone and hold the joint together. It results in inflammation of the joint lining.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
In Rheumatoid Arthritis, the body’s immune system attacks the lining of the joint capsule, a tough membrane that encloses all the joint parts. This lining called the synovial membrane becomes inflamed and swollen. The disease process can eventually destroy cartilage and bone within the joint. Severe Arthritis, particularly if it affects the hands or arms, can make it difficult for you to do daily tasks. Arthritis of weight-bearing joints can keep one from walking comfortably or sitting up straight. In some cases, joints may become twisted and deformed.
Arthritis Treatment
The main focus when treating Arthritis is managing the symptoms and improving joint function. Physical therapy is essential for Arthritis. People with Arthritis often have stiff joints largely because they avoid movements that can increase pain. By not moving arthritic joints, however, the stiffness and pain only get worse. Therefore, people with Arthritis often benefit from physical therapy. Your therapist will teach you how to work out stiffness without further damaging the joint. Ways to reduce strain on the joints during daily activities and modifications for home and workplace environments to reduce motions that may aggravate Arthritis will also be advised. Splints, braces, or assistive devices such as crutches to aid in tasks depending on the type of Arthritis may be recommended if necessary. Personalised exercises and a home training program will be prescribed to improve the range of motion and strengthen the muscles surrounding joints. If in doubt, please seek professional advice.
Osteopathy for Joint Pain and Stiffness
Managing arthritis often involves improving joint mobility and reducing surrounding tension to support daily function. Learn more about how an osteopath in Singapore may assist in addressing symptoms through gentle, individualised treatment approaches.
Check out our popular articles: Diastasis Recti, Tight Back Muscles, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction, Tennis Elbow, Wrist Tendon Injury, Sciatica, Whiplash, Hernia, Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc).