Back Stiffness
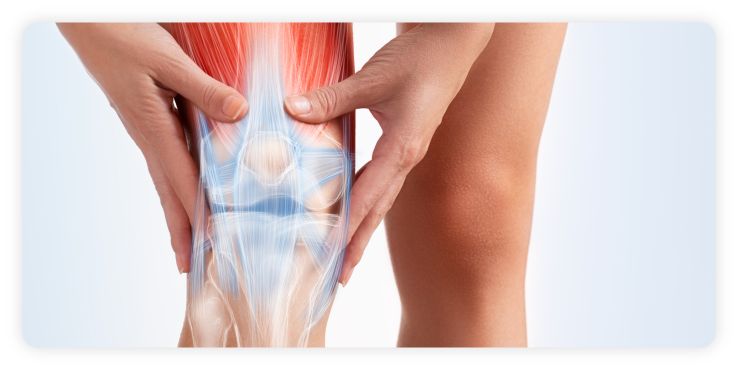
Back stiffness is usually caused by lumbar strain (muscle or ligament strain) or lumbar arthritis. The best way to differentiate the cause of lumbar spine stiffness is the onset of the symptoms. People with stiffness caused by lumbar spine arthritis usually have steadily increased symptoms over the years of a worsening problem. On the other hand, muscular stiffness is usually related to acute trauma (such as lifting a heavy weight incorrectly) in which the back muscles seize up and immobilise the back muscles. Both are common occurrences related in part to advancing age and increasing rates of obesity.
Types of Back Stiffness
When characterising back stiffness with or without acute pain, there are usually two common causes which are lumbar strain and lumbar spine osteoarthritis. A lumbar strain is the most common cause of back stiffness. This problem occurs as a result of an injury to the back muscles and ligaments that support the spinal column. One may or may not remember the initial event that triggered their muscle spasm, but the symptoms of a lumbar muscle strain can be severe. The strain will occur in around the muscles that support the spine specifically in the extensors (back and buttock muscles), flexors (abdominal muscles and hip muscles), and obliques or rotators (side muscles). Lumbar spine osteoarthritis is a progressive condition in which the joints of the vertebrae are damaged by long-term wear and tear. As arthritis progresses, cartilage and discs in the lumbar spine begin to thin and disappear, causing stiffness and pain as bone rubs against bone. This can make movements such as bending, stooping and twisting very difficult. Although not common, other forms of arthritis such as psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can also negatively impact joints including the spine.
For instances where a stiff back happens in the morning, it might be a result of a period of inactivity or due to a rare type of arthritis of the spine called ankylosing spondylitis that causes irritation and swelling between the spine’s discs and, eventually, vertebrae fusing together. This condition occurs more frequently in men and could have a hereditary factor. In such cases, care from a qualified chiropractor in Singapore may help assess spinal alignment and support joint mobility.
Symptoms of Back Stiffness
Whether the back feels tight often or occasionally, it is important to listen to the body and take steps to loosen tension. A tight lower back can worsen and lead to more serious problems. Tightness in the back may be accompanied by pain, spasms and cramping. The pain often feels like a constant, dull ache, and back may feel stiff, tense, and contracted. One may also feel tightness in the pelvis, hips, and legs.
Back Stiffness Treatment
Physical therapy can help with the treatment of Back Stiffness. The main goal of physical therapy is to make everyday tasks and activities easier. Manual therapy will be done to help with back pain and boost flexibility. This will help relax muscles, increase circulation, and eases pain in the soft tissues. Gentle manipulations and mobilisation techniques will be incorporated to twist, pull, or push bones and joints into position to help improve flexibility. Lifestyle recommendations, back stretches, and exercises will then be prescribed as treatment progresses to help relieve lower back stiffness. If in doubt, please seek professional advice.
Chiropractic Care for Back Stiffness
Persistent tightness or stiffness in the back may be linked to posture, muscle imbalance, or spinal joint issues. Learn more about our chiropractic clinic in Singapore and how chiropractic care may help support spinal mobility and overall function.
Check out our popular articles: Diastasis Recti, Tight Back Muscles, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction, Tennis Elbow, Wrist Tendon Injury, Sciatica, Whiplash, Hernia, Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc).