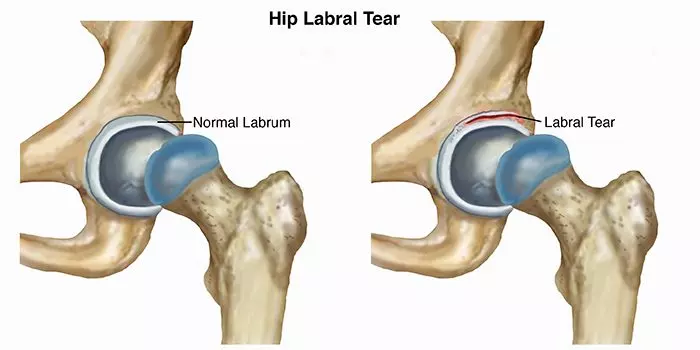
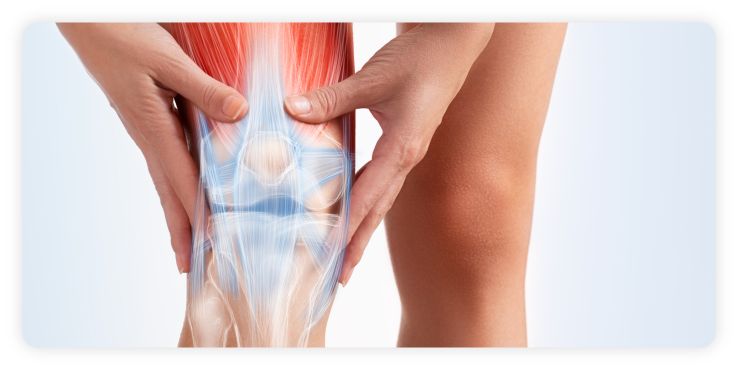
What are Hip Labrum Tears?
A Hip Labrum Tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. The hip is shaped like a ball-and-socket. The socket is called the acetabulum, and the ball is the femoral head, located at the top of the femur (leg bone). A Hip Labral Tear is an injury to the labrum, the soft tissue that covers the acetabulum. The labrum helps the femoral head move smoothly within the socket. It lets the hip move without problems or pain. It also serves as a seal, keeping the ball and socket together but not touching.
What causes Hip Labrum Tears?
Hip Labrum Tears can be caused by many things, including the following structural ailments, injury, and degenerative health conditions. Structural ailments which are conditions that cause abnormal hip movement can also lead to Hip Labrum Tears. In Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI), the femoral head does not fit into the socket properly. This imperfect fit can cause long-lasting groin pain and movement limitations. This is the most common cause of labrum tears. FAI can affect people at any age. Without treatment, it can result in Osteoarthritis. Trauma to the hip can lead to a Hip Labrum Tear. This can happen to people who play certain sports that have repetitive and high-impact movements, such as ice hockey, football, soccer, and golf. Degenerative health conditions such as osteoarthritis can also result in Hip Labrum Tears. Osteoarthritis is a chronic (long-term) wearing down of the cartilage between the joints. As cartilage slowly erodes over time, it becomes more prone to tearing. Older age and excessive weight can increase a person’s risk of developing osteoarthritis. People with Osteoarthritis commonly have pain and stiffness in more than one joint like the hip and knee.
Symptoms of Hip Labrum Tears
Many Hip Labrum Tears cause no signs or symptoms. Some people, however, have one or more of the following pain in the hip or groin often made worse by long periods of standing, sitting, or walking, a locking, clicking, or catching sensation in the hip joint, and stiffness or limited range of motion in the hip joint.
Hip Labrum Tears Treatment
Physical therapy can help with the treatment of Hip Labrum Tears. A physical therapist will help identify and change any external factors causing the pain, such as exercise selection, footwear, or the number of exercises performed. Based on the condition, a physical therapist will design a personalised progressive resistance program including the core (midsection) and lower extremity. Manual therapy techniques will be used to gently move the muscles and joints to decrease pain and improve motion and strength. Self-stretching techniques for the lower body to decrease pressure and help restore normal motion in the back, hip, and leg will also be taught. Exercises that improve range of motion while protecting the area that has the labrum tear will be prescribed. Once the strength and motion improve, functional training will be incorporated. If in doubt, please seek professional advice.
Osteopathy for Hip Labral Tears
Labral tears in the hip can cause pain, stiffness, or a catching sensation during movement. Learn more about how an osteopath in Singapore may assist with managing symptoms and improving hip mobility through tailored, hands-on care.
Check out our popular articles: Diastasis Recti, Tight Back Muscles, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction, Tennis Elbow, Wrist Tendon Injury, Sciatica, Whiplash, Hernia, Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc).