Intercostal Muscle Strain
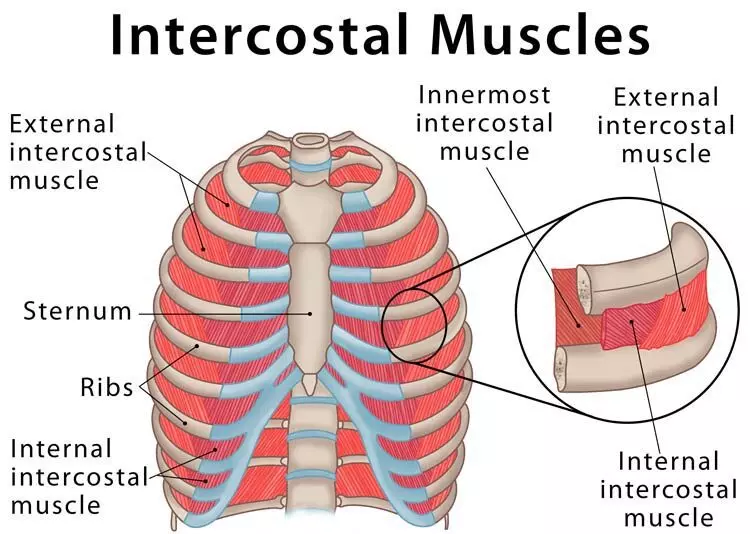
Intercostal Muscle Strain is an injury affecting the muscles between two or more ribs. The intercostal muscles have different layers that are attached to the ribs to help build the chest wall and assist in breathing. When an intercostal muscle gets twisted, strained, or stretched too far, it can tear, causing Intercostal Muscle Strain. About 49% of all musculoskeletal chest pain comes from the intercostal muscles. If you’re experiencing persistent discomfort, a chiropractor in Singapore may help with identifying the source and guiding treatment.
Causes of Intercostal Muscle Strain
Intercostal Muscle Strain most often occurs as a result of an injury or overexertion of the muscles.
Other causes of Intercostal Muscle Strain may include a direct blow to the rib cage, such as from a fall or car accident. Twisting the torso beyond its normal range of motion as well as forceful twisting while lifting weights may also result in this strain. A sudden increase in physical activity can lead to Intercostal Muscle Strain. This is the case particularly when muscles are weakened by a lack of exercise or poor posture.
Symptoms of Intercostal Muscle Strain
Symptoms of Intercostal Muscle Strain may include:
- Sharp upper back and rib pain.
- Severe and sudden pain, particularly if caused by a blow to the chest or back.
- Gradual worsening pain after repetitive movement, such as swimming, or other physical exercises.
- Tenderness in the area between the ribs.
- Muscle rigidity when bending or twisting the upper body.
- Pain when coughing, sneezing, or breathing in deeply.
Intercostal Muscle Strain Treatment
Initial treatment for this type of Muscle Strain must remain conservative to avoid aggravating the condition. Once the initial inflammation has been reduced, physical therapy then helps to restore flexibility to the joints and muscles involved, while improving strength and stability of the spine. Apart from manual therapy, Cryotherapy and therapeutic ultrasound therapy will be included to decrease pain and inflammation of spinal structures. Gentle exercises will also be prescribed to restore joint mobility, range of motion, and strengthen muscles of the back and abdominals. This aims to alleviate the stress placed on the spinal joints, discs, and neck. If in doubt, please seek professional advice.
Need Support for Intercostal Muscle Strain?
If you’re experiencing chest discomfort due to muscle strain, early care can help manage symptoms and aid recovery. Visit our chiropractic clinic in Singapore to explore personalised approaches that may assist with pain relief and improved mobility.
Check out our popular articles: Diastasis Recti, Tight Back Muscles, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction, Tennis Elbow, Wrist Tendon Injury, Sciatica, Whiplash, Hernia, Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc).