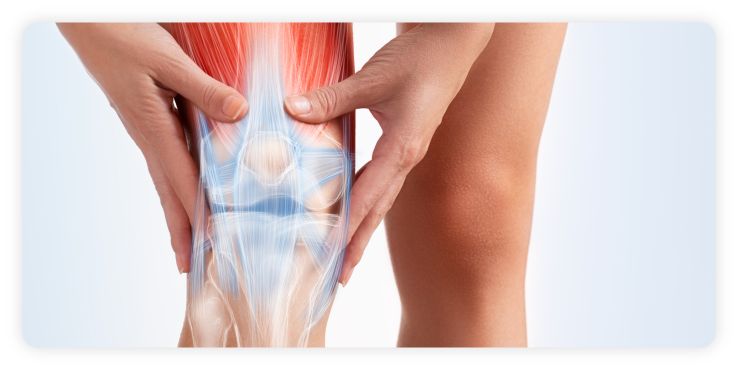
What is Prepatellar Bursitis or Knee Bursitis?
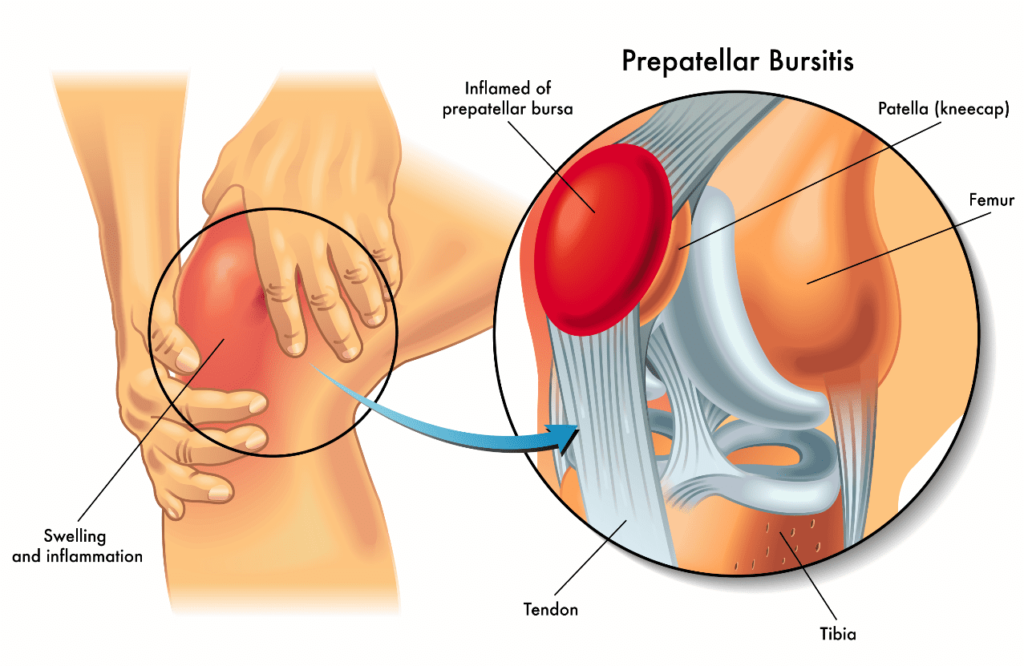
Prepatellar Bursitis or knee bursitis is a swelling of the bursa or small sack of fluid at the front of the patella (kneecap). It can be acute or chronic where it occurs gradually over time.
What causes Prepatellar Bursitis or Knee Bursitis?
Acute Prepatellar Bursitis can be caused by a direct blow or fall on the knee. This ruptures blood vessels that bleed into the bursa causing swelling and triggering an inflammation reaction in the walls of the bursa. Subsequently, the walls may then thicken, causing tenderness that may remain even after the swelling has reduced. Acute Prepatellar Bursitis can also be triggered by an infection as a result of a surface injury, such as a skin wound over the kneecap. In this case, bacteria may spread into the fluid within the prepatellar bursa causing infection. Chronic Prepatellar Bursitis is a longer-term problem that may recur over a period of time. Repeated damage to the knee for example from kneeling or work that involves a lot of pressure on the kneecap thickens the walls of the bursa causing irritation.
Targeted rehabilitation and guided treatment through physiotherapy can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent future flare-ups.
Symptoms of Prepatellar Bursitis or Knee Bursitis
Symptoms of Prepatellar Bursitis include pain and tenderness at the front of the kneecap and just below it. The kneecap or patella may be swollen and warm to the touch. Movements such as kneeling may be painful. If the injury becomes chronic, then there may be a visible tender lump floating underneath the skin on the patella.
Relieve Knee Discomfort with Professional Care
If you’re struggling with swelling, pain, or stiffness in the knee, getting expert support can make a real difference. At our physio clinic in Singapore, you’ll receive personalised care aimed at reducing inflammation, restoring movement, and supporting long-term recovery. With the right treatment plan, you can get back to your routine with greater ease and confidence.
Prepatellar Bursitis or Knee Bursitis Treatment
Physical therapy can help with the treatment of Prepatellar Bursitis. The goal of treatment is to regain mobility and range of motion of the knee. Treatment will include manual therapy, therapeutic ultrasound therapy, and Cryotherapy to help decrease pain and inflammation of the prepatellar bursa. Specific stretching and strengthening exercises will be prescribed by your therapist to aid in re-attaining range of motion and strengthen muscles of the knee to support, stabilise and decrease the stresses placed on the prepatellar bursa and tendons of the knee joint. Functional training will also be taught to avoid recurrence of pain, especially when carrying out daily activities. If in doubt, please seek professional advice.
Check out our popular articles: Diastasis Recti, Tight Back Muscles, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction, Tennis Elbow, Wrist Tendon Injury, Sciatica, Whiplash, Hernia, Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc).