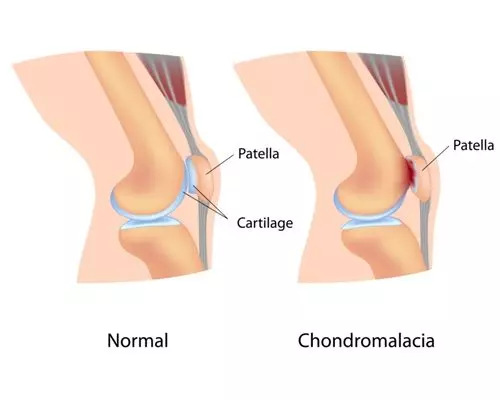
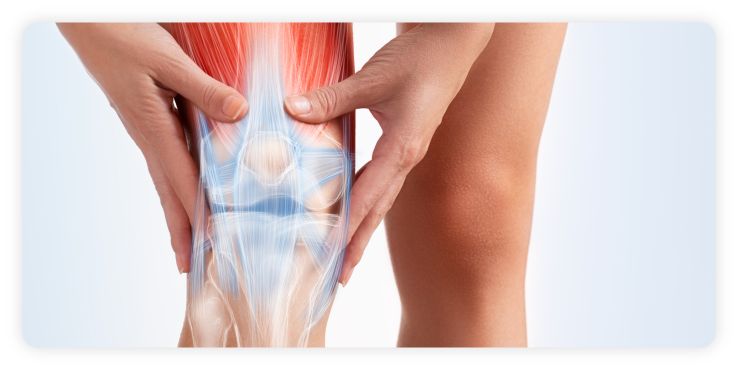
What is Patella Pain (Chondromalacia Patella)?
Chondromalacia Patella, also known as “Runner’s Knee”, is one of the most common causes of chronic knee pain. It is an abnormal softening of the cartilage of the underside of the patella (knee cap) due to pain in the front of the knee. Chondromalacia patella results from degeneration of cartilage due to poor alignment of the patella as it slides over the lower end of the thigh bone (femur). This process is sometimes referred to as Patellofemoral Syndrome. The pain of chondromalacia patellae is aggravated by activity or prolonged sitting with bent knees. Abnormal “tracking” or “maltracking” toward the lateral (outer) side of the femur causes the patella to grate over the lower end of the femur causing chronic inflammation and pain. In many cases, physiotherapy in Singapore may help improve knee alignment, strengthen surrounding muscles, and manage symptoms effectively.
Symptoms of Patella Pain (Chondromalacia Patella)
The symptoms of chondromalacia patella are generally a vague discomfort of the inner front of the knee, aggravated by activity (running, jumping, climbing, or descending stairs) or by prolonged sitting with knees in a moderately bent position. Tightness or fullness may also be felt in the knee area. Occasionally, if chronic symptoms are ignored, the associated loss of quadriceps muscle strength may cause the leg to give out. Besides an obvious reduction in quadriceps muscle mass, mild swelling of the knee area may occur.
Patella Pain (Chondromalacia Patella) Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce the pressure on the patella and joint. Resting, stabilising, and icing the joint may be the first line of treatment. The cartilage damage resulting in Runner’s Knee can often repair itself with rest. Several weeks of anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen to reduce inflammation around the joint may be prescribed by a doctor.
Physical therapy is often recommended for treatment of pain and dysfunction associated with Patellofemoral Syndrome and Chondromalacia of the patella. Physical therapy focusing on strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, adductors, and abductors can help improve muscle strength and balance. Muscle balance will help prevent knee misalignment. Additionally, isometric exercises that involve tightening and releasing the muscles can help to maintain muscle mass. Kinesio taping of the kneecap (patella) may also be done to reduce pain as it helps alter the alignment or the way the patella moves. If in doubt, seek professional advice.
Physiotherapy for Patellofemoral Pain
Addressing patella pain often involves improving muscle balance and joint tracking around the knee. Learn more about how care at our physio clinic in Singapore may support recovery through targeted exercises and movement strategies tailored to your needs.
Check out our popular articles: Diastasis Recti, Tight Back Muscles, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction, Tennis Elbow, Wrist Tendon Injury, Sciatica, Whiplash, Hernia, Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc).